Publikationen Rieger
-
A functional clock in only two dorsal clock neurons is sufficient to restore the basal circadian activity pattern of Drosophila melanogaster.. . In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 122(44), p. e2506164122. 2025.
- [ URL ]
-
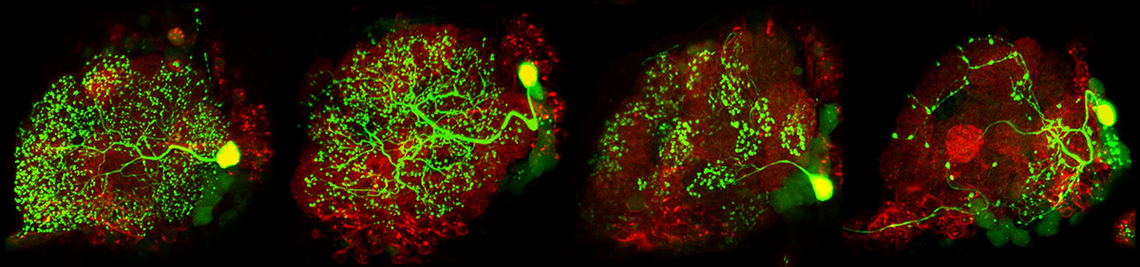
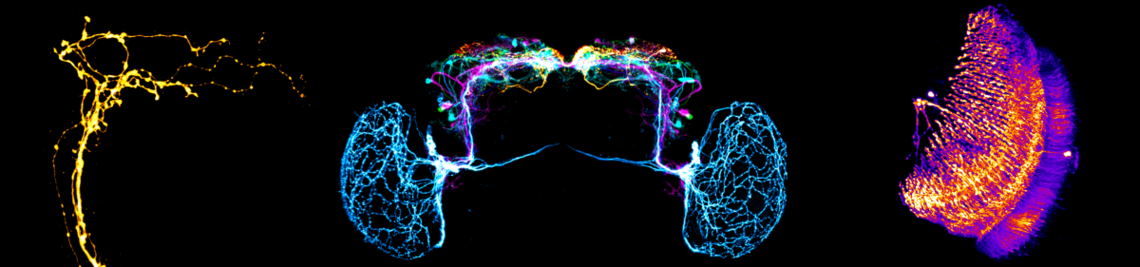
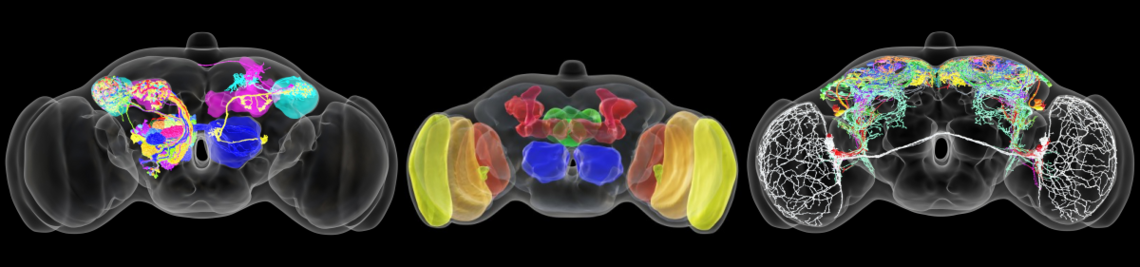
Synaptic connectome of the Drosophila circadian clock. . In Nature Communications, 15(1), p. 10392. 2024.
- [ URL ]
-
A clock for all seasons. . In Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 210(4), pp. 473–480. 2024.
- [ URL ]
-
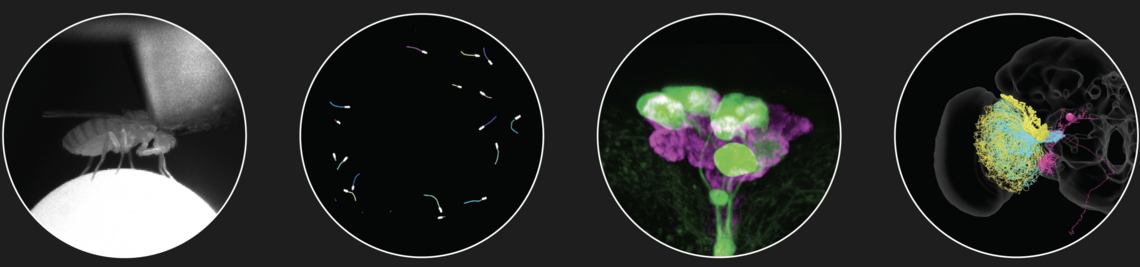
A new Activity Monitor for Aquatic Zooplankter (AMAZE) allows the recording of swimming activity in wild-caught Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). . In Scientific Reports, 14(1), p. 16963. 2024.
- [ URL ]
-
A Detailed Re-Examination of the Period Gene Rescue Experiments Shows That Four to Six Cryptochrome-Positive Posterior Dorsal Clock Neurons (DN1p) of Drosophila melanogaster Can Control Morning and Evening Activity. . In Journal of Biological Rhythms. 2024.
- [ URL ]
-
The neuropeptide pigment-dispersing factor signals independently of Bruchpilot-labelled active zones in daily remodelled terminals of Drosophila clock neurons. . In European Journal of Neuroscience, 59, pp. 2665–2685. 2024.
- [ URL ]
-
Two light sensors decode moonlight versus sunlight to adjust a plastic circadian/circalunidian clock to moon phase. . In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(22), p. e2115725119. 2022.
- [ URL ]
-
The lateral posterior clock neurons of Drosophila melanogaster express three neuropeptides and have multiple connections within the circadian clock network and beyond. . In Journal of Comparative Neurology, n/a(n/a). 2022.
- [ URL ]
-
The Neuronal Circuit of the Dorsal Circadian Clock Neurons in Drosophila melanogaster. . In Frontiers in Physiology, 13. 2022.
- [ URL ]
-
Loss of p21-activated kinase Mbt/PAK4 causes Parkinson-like phenotypes in Drosophila. . In Disease Models & Mechanisms, 14(6). 2021.
- [ URL ]
-
Natural Zeitgebers Under Temperate Conditions Cannot Compensate for the Loss of a Functional Circadian Clock in Timing of a Vital Behavior in Drosophila. . In Journal of Biological Rhythms. 2021.
- [ URL ]
-
Natural Zeitgebers Under Temperate Conditions Cannot Compensate for the Loss of a Functional Circadian Clock in Timing of a Vital Behavior in Drosophila. . In J Biol Rhythms, 36(3), pp. 271–285. 2021.
-
Loss of function in the Drosophila clock gene period results in altered intermediary lipid metabolism and increased susceptibility to starvation. . In Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 77, pp. 4939–4956. 2020.
- [ URL ]
-
Single-cell resolution long-term luciferase imaging in cultivated Drosophila brains.. . 2020.
- [ URL ]
-
The Circadian Clock Improves Fitness in the Fruit Fly, Drosophila melanogaster. . In Frontiers in Physiology, 10, p. 1374. 2019.
- [ URL ]
-
The Circadian Clock Improves Fitness in the Fruit Fly, Drosophila melanogaster. . In Front Physiol, 10, p. 1374. 2019.
-
Role of Rhodopsins as Circadian Photoreceptors in the Drosophila melanogaster. . In Biology, 8(1), p. 6. 2019.
- [ URL ]
-
Neuroanatomical details of the lateral neurons of Drosophila melanogaster support their functional role in the circadian system. . In J Comp Neurol, 526(7), pp. 1209–1231. 2018.
- [ URL ]
-
Cryptochrome interacts with actin and enhances eye-mediated light sensitivity of the circadian clock in Drosophila melanogaster. . In Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 11, p. 238. 2018.
- [ URL ]
-
The Drosophila microbiome has a limited influence on sleep, activity, and courtship behaviors. . In Scientific reports, 8(1), p. 10646. 2018.
- [ URL ]
-
Swing Boat: Inducing and Recording Locomotor Activity in a Drosophila melanogaster Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. . In Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 11, p. 159. 2017.
- [ URL ]
-
Drosophila Rhodopsin 7 can partially replace the structural role of Rhodopsin 1, but not its physiological function. . In Journal of Comparative Physiology A, pp. 1–11. 2017.
- [ URL ]
-
The timed depolarization of morning and evening oscillators phase shifts the circadian clock of Drosophila. . In J Biol Rhythms, 31(5), pp. 428–442. 2016.
- [ URL ]
-
Identification and structural characterization of interneurons of the Drosophila brain by monoclonal antibodies of the Würzburg Hybridoma Library. . In PLOS ONE, 8(9), pp. 1–9. 2013.
- [ URL ]
-
Drosophila clock neurons under natural conditions. . In J Biol Rhythms, 28(1), pp. 3–14. 2013.
- [ URL ]
-
GABA(B) receptors play an essential role in maintaining sleep during the second half of the night in Drosophila melanogaster. . In J Exp Biol, 216(Pt 20), pp. 3837–3843. 2013.
- [ URL ]
-
Two clocks in the brain. . In Progress in Brain Research, pp. 59–82. Elsevier {BV}, 2012.
- [ URL ]
-
Chapter 4 - Two clocks in the brain: An update of the morning and evening oscillator model in Drosophila. . In The Neurobiology of Circadian Timing, Vol. 199, M. M. {Andries Kalsbeek, R. G. Foster (eds.), pp. 59–82. 2012.
- [ URL ]
-
The ability to entrain to long photoperiods differs between 3 Drosophila melanogaster wild-type strains and is modified by twilight simulation. . In J Biol Rhythms, 27(1), pp. 37–47. 2012.
-
The dual-oscillator system of Drosophila melanogaster under natural-like temperature cycles. . In Chronobiol Int, 29(4), pp. 395–407. 2012.
-
The nocturnal activity of fruit flies exposed to artificial moonlight is partly caused by direct light effects on the activity level that bypass the endogenous clock. . In Chronobiol Int, 26(2), pp. 151–166. 2009.
-
Period gene expression in four neurons is sufficient for rhythmic activity of Drosophila melanogaster under dim light conditions. . In J Biol Rhythms, 24(4), pp. 271–282. 2009.
-
The Lateral and Dorsal Neurons {ofDrosophila} melanogaster:New Insights about Their Morphology and Function. . In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, 72(1), pp. 517–525. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2007.
- [ URL ]
-
Glutamate and its metabotropic receptor {inDrosophilaclock} neuron circuits. . In J Comp Neurol, 505(1), pp. 32–45. 2007.
- [ URL ]
-
The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster favors dim light and times its activity peaks to early dawn and late dusk. . In J Biol Rhythms, 22(5), pp. 387–399. 2007.
- [ URL ]
-
Moonlight shifts the endogenous clock of Drosophila melanogaster. . In Proc Natl Acad Sci, 104(9), pp. 3538–3543. 2007.
-
Hofbauer-Buchner Eyelet Affects Circadian Photosensitivity and Coordinates {TIM} and {PER} Expression in Drosophila Clock Neurons. . In J Biol Rhythms, 22(1), pp. 29–42. 2007.
- [ URL ]
-
Development and morphology of the clock-gene-expressing lateral neurons of Drosophila melanogaster. . In J Comp Neurol, 500(1), pp. 47–70. 2006.
- [ URL ]
-
Functional analysis of circadian pacemaker neurons in Drosophila melanogaster. . In J Neurosci, 26(9), pp. 2531–2543. 2006.
-
Cryptochrome, compound eyes, Hofbauer-Buchner eyelets, and ocelli play different roles in the entrainment and masking pathway of the locomotor activity rhythm in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. . In J Biol Rhythms, 18(5), pp. 377–391. 2003.
- [ URL ]