Role of the vacuole in nutrient balance
Anion uptake systems in plant cells
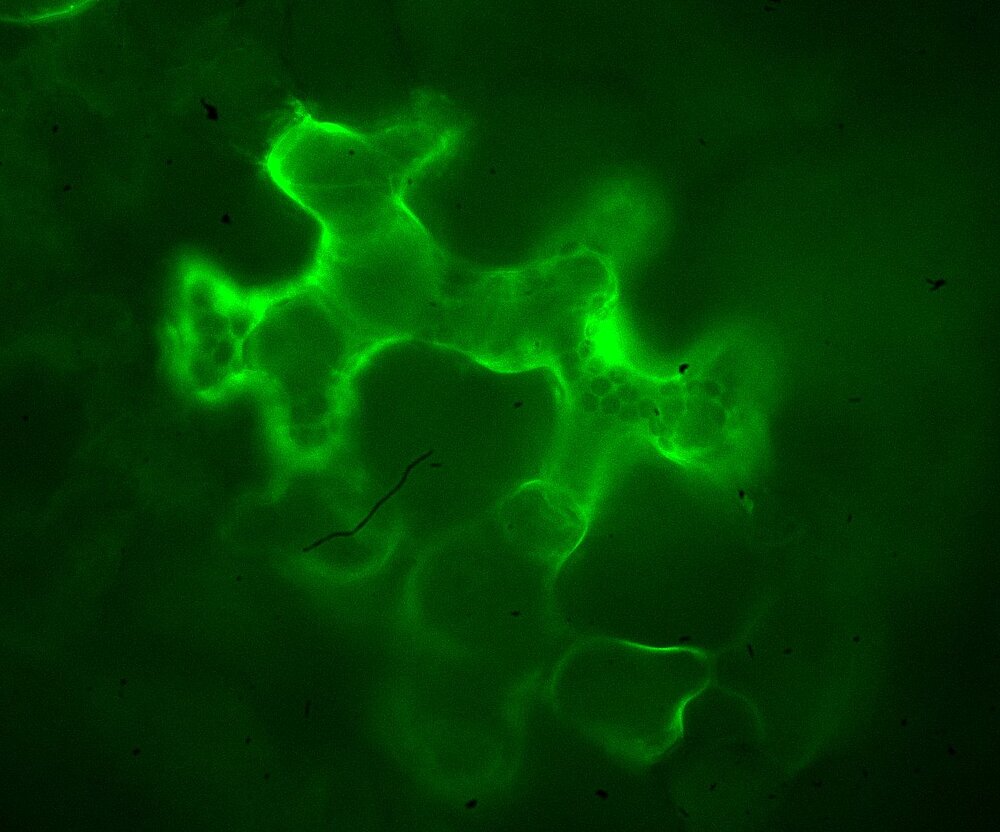
Plants need to accumulate relative large quantities of nitrate (NO3-) and phosphate (PO43-) from the soil to enable the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). In addition, plants can take of Cl-, but they only need small amounts of this anion for optimal growth. Because of over-fertilization, many soils in Germany show high levels of NO3- and Cl- and there is a demand to reduce the NO3- levels, in order to keep the protect groundwater.
In collaboration with the group of Prof. Dr. C-M Geilfus (Plant Nutrition & Soil Science, University of Geisenheim) we study the role of Cl- and NO3- in growth of bean and barley plants, and the regulation of stomatal movements in these species. We are focusing on the biophysical properties and molecular nature of anion uptake transport proteins in guard cells. Our results will help to understand how plants can cope with high Cl- and low NO3- levels in the soil, which are conditions that are likely to develop in agricultural soils, in the near future.